If you’re a beginner in trading, technical analysis can seem challenging to understand. I went through the same experience when I first started learning trading.
I was confused by trendline, trend, support, and resistance, etc. But as I understood them one by one, they slowly became so easy.
And that’s why, in this blog post, we’ll discuss the four most important topics in the stock market that every trader should know.
There are four important topics that you should keep in mind while trading: Support and Resistance, Market Structure/Trend, Time frame, and Trendline.
By the end of this post, you’ll have a better understanding of these concepts and be able to apply them to your trading. So, let’s get started!
4 Important Topics to Know as a Beginner
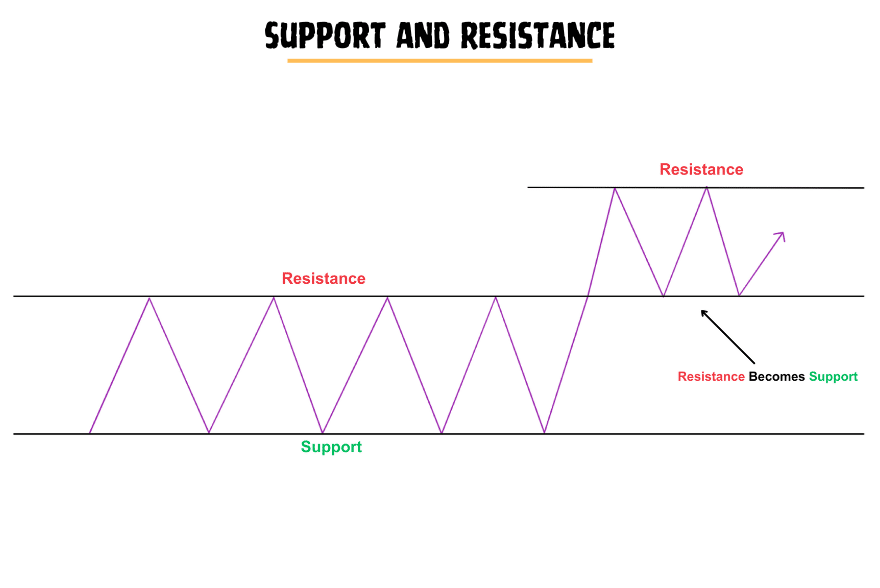
Support and Resistance
Support and resistance are two essential concepts traders use in technical analysis to identify potential price levels at which the market may change direction.
What is Support?
Support is an important level on a chart where the price stops and resists further fall. This happens because demand is higher than supply at this level, which shows more buyers are entering the market than sellers. As a result, the price starts to go up again.
What is Resistance?
Resistance is an important level on a chart where the price faces rejection and can’t go up anymore.
This happens because supply is higher than demand at this level, which shows more sellers are entering the market than buyers. As a result, the price starts to fall.
Traders frequently use support and resistance levels to determine possible trade entry and exit points.
If the price is approaching a support level, a trader may look to buy the asset, anticipating a bounce back up.
If the price approaches a resistance level, a trader may look to sell the asset, anticipating a decline.
It’s important to note that support and resistance levels are not always the same and can sometimes be breached.
However, they can still be helpful as a general guide for identifying potential market turning points.
Market Structure/Trend
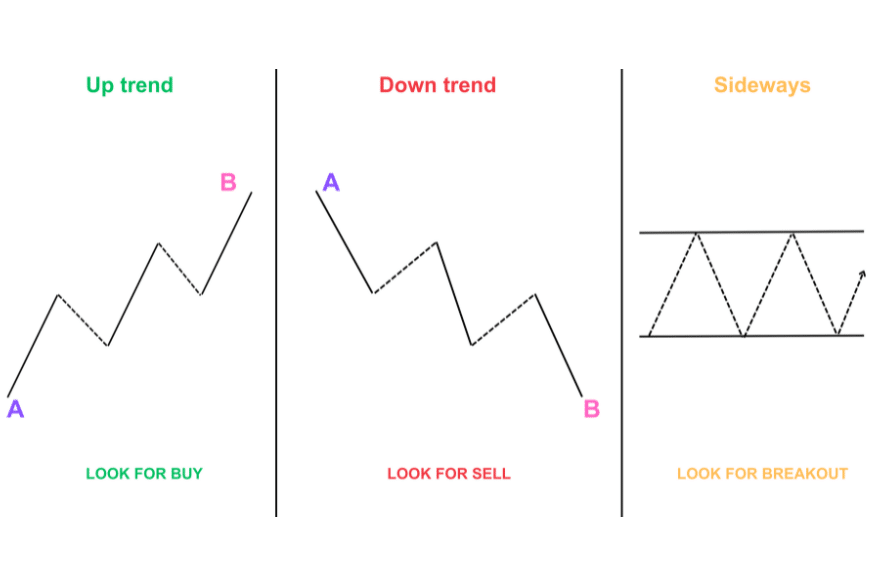
Trends in trading refer to the general direction that markets are moving towards over some time.
These trends can be classified into three categories: uptrend, downtrend, and sideways trend.
What is an Uptrend?
An uptrend occurs when prices consistently form higher highs (HH) and higher lows (HL) in the market.
Sometimes, higher highs do not form, but unless the higher low has not broken, it’s still an uptrend.
What is a Downtrend?
A downtrend is a market structure in which lower lows (LL) and lower highs are formed.
Sometimes lower lows are not formed, but as long as lower highs form, it’s still a Downtrend.
What is Sideways Trend?
In a sideways trend, the market is moving within a range with no clear direction. This indicates a balance between supply and demand, and buyers and sellers are evenly matched.
A sideways trend is also known as ‘consolidation.’ It is a market structure where stock gets stuck within a price range. We look for a breakout when a stock is in consolidation.
Understanding trends in trading is important because it can help traders decide when to buy and sell assets.
By identifying trends, traders can determine whether an investment is likely to continue moving in a specific direction or reverse course and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
Time Frame
Timeframe is another important concept in trading that refers to the time displayed on a price chart. Different traders may use different timeframes depending on their trading style and strategy.
Some common timeframes used in trading include daily, weekly, and monthly charts and intraday charts such as 5-minute, 15-minute, 30-minute, and 1-hour charts.
Each timeframe can provide different information about the market, and traders may use multiple timeframes to get a better understanding of the overall trend.
For example, a trader may use a daily chart to identify the long-term trend and a 15-minute chart to look for short-term trading opportunities.
Understanding the timeframe can also help traders determine the appropriate risk-reward ratio for their trades.
Short-term traders may look for smaller price movements and take smaller profits, while long-term traders may be more willing to hold positions for longer periods and take larger profits.
By analyzing multiple timeframes, traders can gain a complete market picture and make more accurate predictions about future price movements.
Trend Line
Trend lines are a technical analysis tool traders use to identify the direction of a trend and potential reversal points.
The trendline is the simple line drawn on a chart that helps us identify a specific trend’s support level. In short, a trendline is a tool that shows ongoing trends.
There are two types of trendlines: Bullish Trendline and Bearish Trendline.
A Bullish Trendline
In an uptrend, the Bullish trend line acts as a support level, indicating that the price is likely to continue moving up as long as it stays above the trend line.
A Bearish Trendline
In a downtrend, the trend line acts as a resistance level, indicating that the price is likely to continue moving down as long as it stays below the trend line.
Traders often use trend lines with other technical analysis tools, such as support and resistance levels, to help them make trading decisions.
By identifying the trend direction and potential reversal points, traders can enter or exit trades at the right time and maximize their profits.
However, it’s important to note that trend lines are unreliable and sometimes broken, so traders should use them with other indicators to confirm their analyses.
Conclusion
Technical analysis is an essential part of trading, and understanding the four critical topics discussed in this post can help traders make the right decisions and improve their trading.
Support and resistance levels, market structure/trend, timeframe, and trendline are essential concepts that traders should consider while analyzing the market.
By learning these concepts, traders can identify potential trade entry and exit points, predict future price movements, and make better trading decisions.